Go 的 map 作为该语言最常见的基础数据结构之一。
源码解读
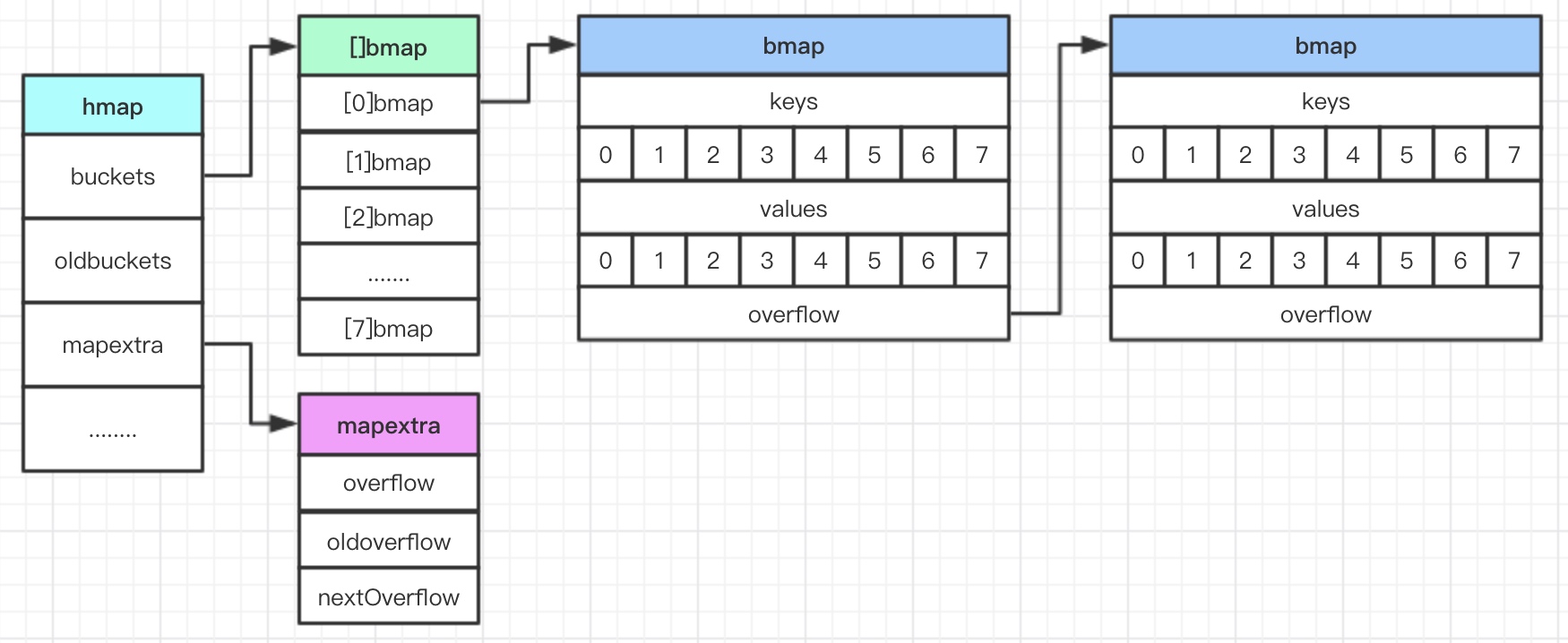
Go 语言实现的 map 并非是完全的哈希 map ,是一种类似两层树状的结构,根据 key 的哈希值的低八位 决定第一层的位置,根据高八位决定第二层,如果第二层所在冲突了则会有一个额外的位置 用于存储哈希碰撞的 kv。看图会帮助理解:
图解:

数据结构
源码在 go/src/runtime/map.go 文件中:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| // map 的实现
type hmap struct {
count int // 已使用位置数(即 len() 方法会返回该值),之所以说已使用的是因为并非所有的位置都存放位置
flags uint8 // map的状态,通过该字段判断当前是否被某个进程进行写操作
B uint8 // 2^B 为桶的数量, B为 3 时 2^3 一共 8 个桶
noverflow uint16 // 溢出的桶数量
hash0 uint32 // hash seed
buckets unsafe.Pointer // 桶的数组
oldbuckets unsafe.Pointer // 旧桶的数组。map 扩容时 原 buckets 变成 oldbuckets 并将数据逐步迁移,并非一次性迁移
nevacuate uintptr // 扩容进度记录
extra *mapextra // 额外信息。存储非指针数据(为了优化空间)
}
type mapextra struct {
// 为了优化空间 将非指针数据存储在 mapextra里
overflow *[]*bmap // 对应 hmap.buckets
oldoverflow *[]*bmap // 对应 hmap.oldbuckets
// 指向下一个空闲的 bucket
nextOverflow *bmap
}
// bucket 即桶
type bmap struct {
// tophash 存储每个 key 的 tophash 即 key 的前八位,用于判断读取的 key 是否在当前桶里。
tophash [bucketCnt]uint8
// 之后是 key-value 的格子,每个桶最多只能存 8 个且 以 key1...key8value1...value8 的形式存储。
// 还有一个 overflow 用于指向下一个桶。
}
|
读取
按 key 读取
遍历
写入
删除
coming soon